RALEIGH — North Carolina State Fire Marshal Brian Taylor announced the release of emergency rules aimed at aiding Hurricane Helene survivors to utilize temporary housing situations. The announcement came in a press release issued Dec. 11.
“The Office of State Fire Marshal (OSFM) reaffirms its commitment to supporting local governments in their efforts to provide safe and warm shelter for North Carolinians this winter,” the press release says.
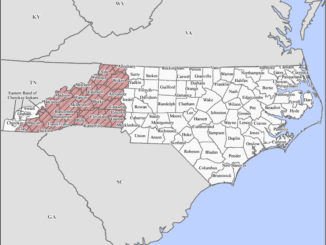
The emergency rule speeds up temporary housing permitting and inspections in the 25 North Carolina counties affected by Hurricane Helene by streamlining the process.
The rule applies to Alexander, Alleghany, Ashe, Avery, Buncombe, Burke, Caldwell, Catawba, Clay, Cleveland, Gaston, Haywood, Henderson, Jackson, Lincoln, Macon, Madison, McDowell, Mitchell, Polk, Rutherford, Transylvania, Watauga, Wilkes and Yancey counties, plus the Eastern Band of Cherokee Indians.
To take advantage of the emergency rule, individuals need to fill out and sign an affidavit that limits occupancy to 180 days, after which the building reverts back to needing to comply with standard building codes. Additionally, the owners are required to assume all liability for construction and use of the temporary housing structure.
Under the emergency rule, temporary housing without electrical systems is exempt from permits and inspections, and those exemptions last for the duration of the state of emergency. Housing with electrical systems must be inspected by an electrical inspector before being activated.
Temporary housing must adhere to local zoning regulations and be strategically positioned. The temporary structures are limited to one story, cannot exceed 400 square feet and should be situated as much as possible away from hazardous areas such as flood zones and steep slopes. Additionally, a minimum of 10 feet of separation from property lines to ensure safety and compliance is required.
Each temporary housing unit must meet specific livability requirements. This includes maintaining a minimum ceiling height of 6-foot-8, providing at least one egress door at least 32 inches wide, and ensuring emergency escape windows in sleeping areas.
Additionally, smoke and carbon monoxide alarms are mandatory, and the structure must have heating facilities capable of maintaining a temperature of 68 degrees. Natural ventilation is also required, with window and door openings specifications to ensure adequate air circulation and emergency exit routes.
The fire marshal’s emergency rule provides detailed specifications for the construction of temporary housing units, including precise requirements for foundations, floor joists, wall framing and roof construction.
There are also specific guidelines for electrical systems, with provisions for inspection before activating those systems.
The construction must use approved materials and techniques, such as minimum wood structural panel thicknesses for sheathing, proper nailing patterns, and bracing specifications to ensure structural integrity and basic safety.